Microservices & Nanoservices in the LLM and Agentic Era
Why modular architectures like microservices and nanoservices are essential for LLM efficiency, token optimization, and agent orchestration.
Microservices and Nanoservices in the LLM and Agentic Era
In the evolving landscape of software development, two key forces are converging to reshape application architecture: LLM-powered code generation and agentic AI approaches, where autonomous agents orchestrate workflows by calling APIs and chaining services.
To fully leverage these trends — especially in environments where API calls directly influence token usage and cost efficiency — organizations must rethink how they design their systems. This is where microservices and nanoservices architectures step into the spotlight.
What Are Microservices and Nanoservices?
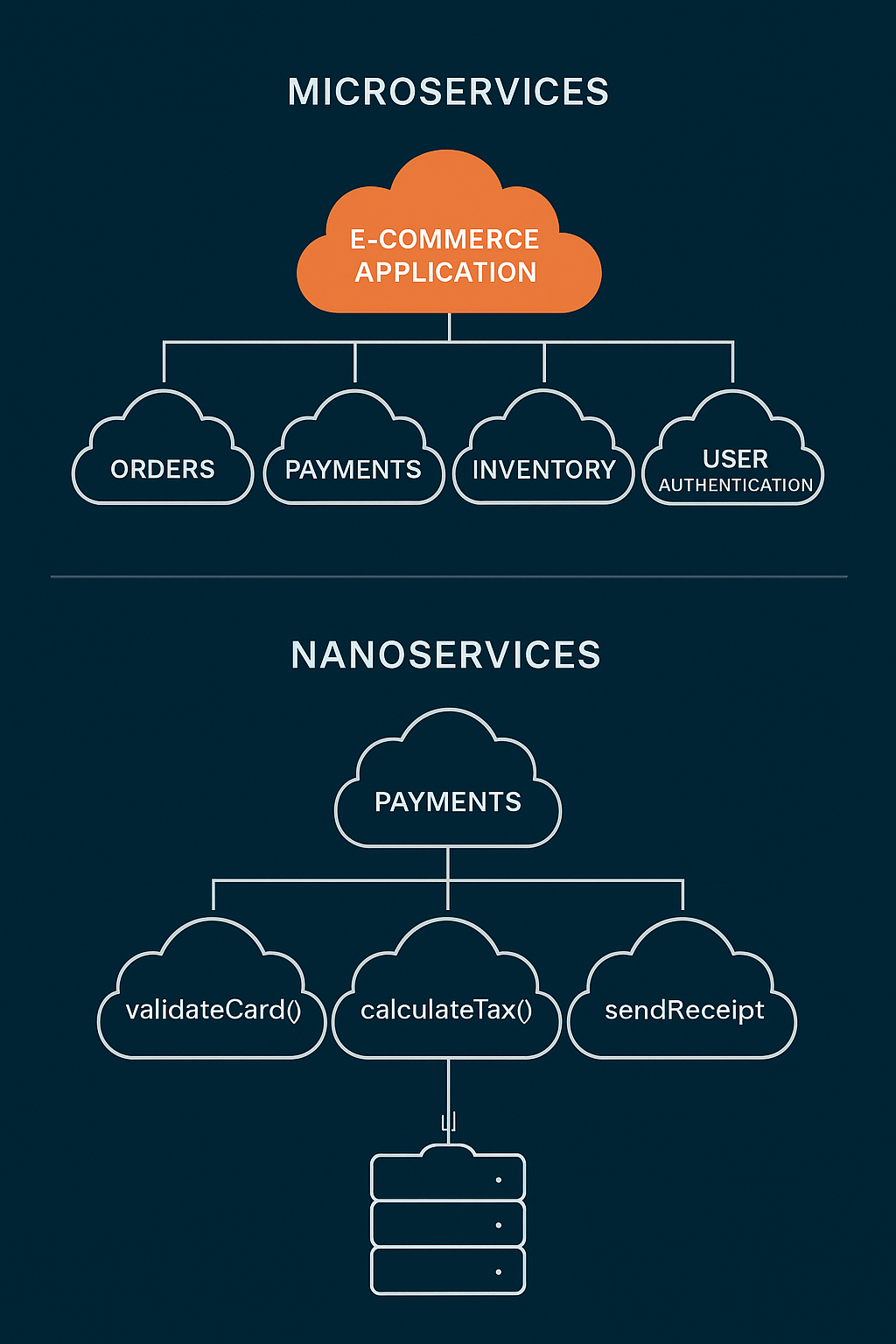
A microservice is a small, autonomous service responsible for a specific business capability. Instead of a single, monolithic codebase, applications are composed of many loosely coupled services that communicate via APIs.
Example: In an e-commerce platform, you might have separate microservices for orders, payments, inventory, and user authentication.
A nanoservice is an even smaller, more specialized unit of functionality. It typically performs one single, well-defined task and is deployed independently — often as a serverless function.
Example: A payment microservice might be broken down into nanoservices for validateCard(), calculateTax(), and sendReceipt(). In serverless platforms like Supabase, these are often implemented as Edge Functions.
Why This Architecture Matters in the LLM & Agentic Era
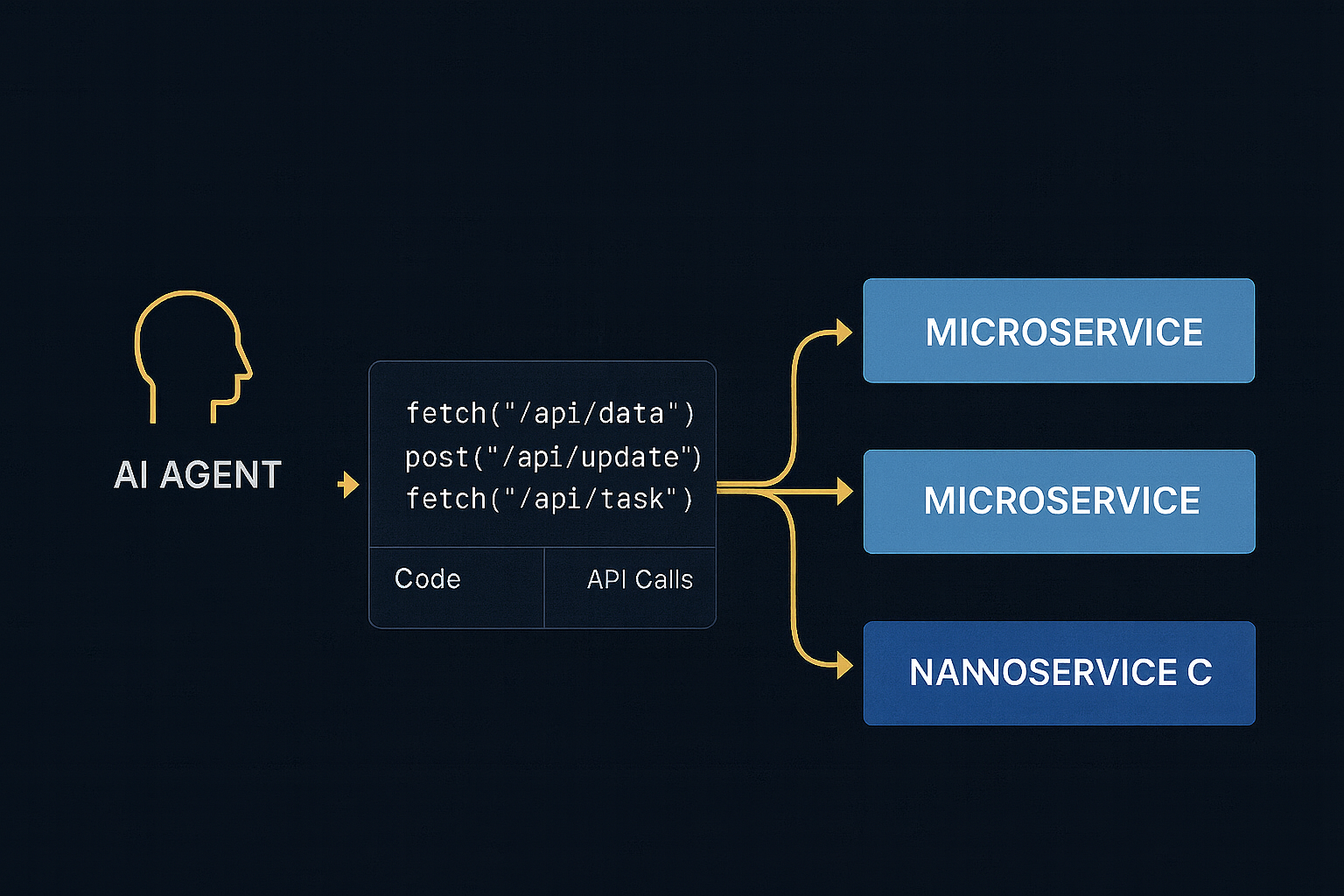
When AI agents (LLM-powered) execute tasks, they often generate code snippets on the fly, make API calls to retrieve or manipulate data, and chain multiple calls to accomplish a goal.
In this environment, tokens equal money, and API calls impact performance. The architecture must support minimal payloads to reduce token usage, precise endpoints so agents call exactly what they need, and parallel execution for efficiency.
A monolith forces the LLM to consume large payloads or navigate unnecessary logic. A nanoservice approach gives the AI surgical precision.
REST Architecture as the AI-Agent Friendly Layer
While GraphQL and event-driven architectures are gaining traction, REST remains the simplest, most predictable interface for LLM agents.
Advantages include: clear contracts with defined URLs and methods, human and machine readability, and stateless calls for scalability.
For LLM integration, a RESTful nanoservice like POST /calculate-tax is much easier to handle than a monolithic /checkout endpoint that does dozens of unrelated things.
Use Case : Lovable + Supabase = Nano-Friendly AI Stack
Lovable, a modern no-code/low-code builder, integrates seamlessly with Supabase — a backend-as-a-service platform offering serverless edge functions, Postgres with real-time subscriptions, and authentication APIs.
Imagine building an AI-driven SaaS with Lovable and Supabase: Lovable generates your frontend UI from natural language prompts, Supabase Edge Functions act as nanoservices solving specific needs for the AI agent, and the LLM calls these functions directly via REST APIs.
This setup allows fast iteration, lower operational costs with serverless pricing, and better control over AI-agent interactions.
Lovable: A no-code/low-code platform that generates full-stack applications from natural language prompts.
Supabase: An open-source backend-as-a-service offering Postgres, authentication, storage, and serverless edge functions.
Why Continue With Microservices & Nanoservices Now
Sticking to a modular service-oriented design is essential because it enables token cost control, ensures security by restricting AI to safe endpoints, simplifies governance, and scales AI orchestration.
Microservices and nanoservices allow for parallel handling of dozens of agent requests without bottlenecks.
In 2025, LLMs and AI agents are not just consuming APIs — they are driving software execution. To make them efficient, controllable, and cost-effective, architectures must evolve toward microservices and nanoservices.
The Lovable + Supabase model demonstrates how serverless nanoservices can power an AI-native application stack, keeping agility high and costs low.
Your architecture isn’t just for humans anymore — it’s for the AI agents that will run your business logic.

